does high blood sugar cause ketoacidosis Sglt2 inhibitor-induced euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis
The ketogenic diet has gained immense popularity in recent years, and for good reason. It has been shown to produce significant weight loss, improve athletic performance, and even improve mental clarity. Essentially, the keto diet is a low-carbohydrate, high-fat diet that forces the body to burn fat for energy rather than carbohydrates. One key element of the ketogenic diet is achieving a state of ketosis. Ketosis is a metabolic state in which the body burns fat for fuel instead of carbohydrates. It is achieved by reducing the intake of carbohydrates and increasing the intake of healthy fats. To understand ketosis in more detail, it is important to understand how the body normally produces energy. Normally, the body breaks down carbohydrates into glucose, which is then used as the primary source of energy. However, when carbohydrate intake is limited, the body begins to break down fat for energy instead. This process results in the production of ketones, which are a type of molecule that can be used for fuel. Achieving a state of ketosis can have many benefits. For one, it can lead to rapid weight loss, as the body is forced to break down stored fat for energy. Additionally, it can improve athletic performance by providing a sustained source of energy during exercise. Some research has even suggested that ketosis may have neuroprotective effects and could help improve brain function. However, it is important to note that achieving a state of ketosis can be difficult and may come with potential side effects. Some people may experience headaches, nausea, and fatigue during the initial stages of the diet. Additionally, those with certain medical conditions may not be suitable candidates for the keto diet, such as individuals with pancreatitis or liver disease. It is also important to be mindful of the types of fats consumed on the keto diet. While healthy fats such as avocados, nuts, and olive oil are encouraged, it is also possible to consume unhealthy saturated and trans fats, which can increase the risk of heart disease and other health issues. In conclusion, the ketogenic diet and achieving a state of ketosis can have many potential benefits for overall health and well-being. However, it is important to carefully follow the guidelines of the diet and be aware of any potential side effects or complications. Consulting with a medical professional before beginning the diet is also encouraged, especially for those with pre-existing medical conditions.
If you are searching about Diabetes and Fruity Breath: Causes, Risks, And Treatment you’ve came to the right place. We have 5 Pictures about Diabetes and Fruity Breath: Causes, Risks, And Treatment like Blood Sugar Guide: does high blood sugar cause ketoacidosis, Diabetes and Fruity Breath: Causes, Risks, And Treatment and also Blood Sugar Guide: does high blood sugar cause ketoacidosis. Read more:
Diabetes And Fruity Breath: Causes, Risks, And Treatment
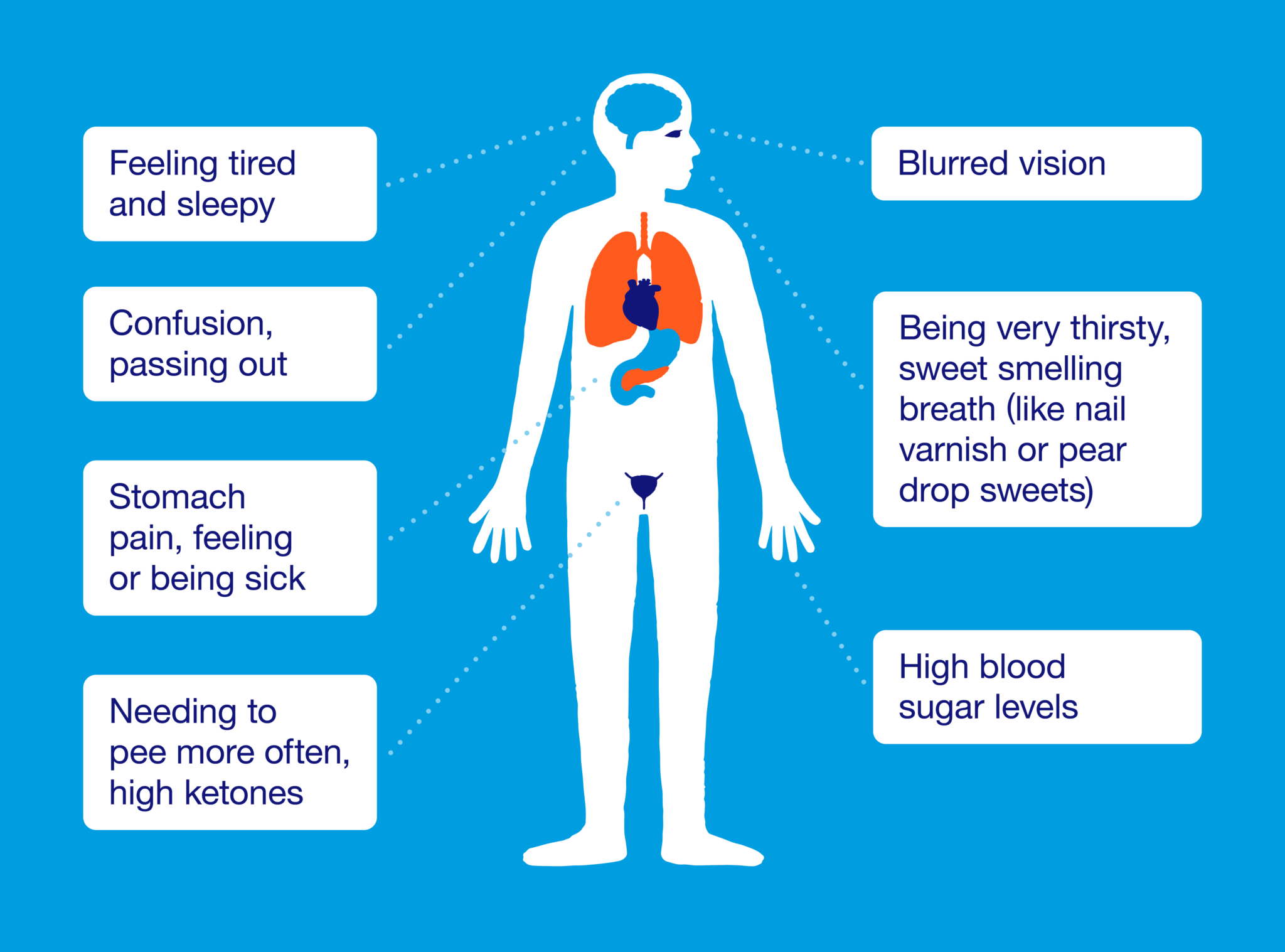 mantracare.orgketoacidosis diabetic dka treatment breath complications fruity ketosis mellitus symptome ketones urine nausea mantracare anzeichen abdominal ursachen medication difficulty remedies
mantracare.orgketoacidosis diabetic dka treatment breath complications fruity ketosis mellitus symptome ketones urine nausea mantracare anzeichen abdominal ursachen medication difficulty remedies
SGLT2 Inhibitor-induced Euglycemic Diabetic Ketoacidosis - Renal Fellow
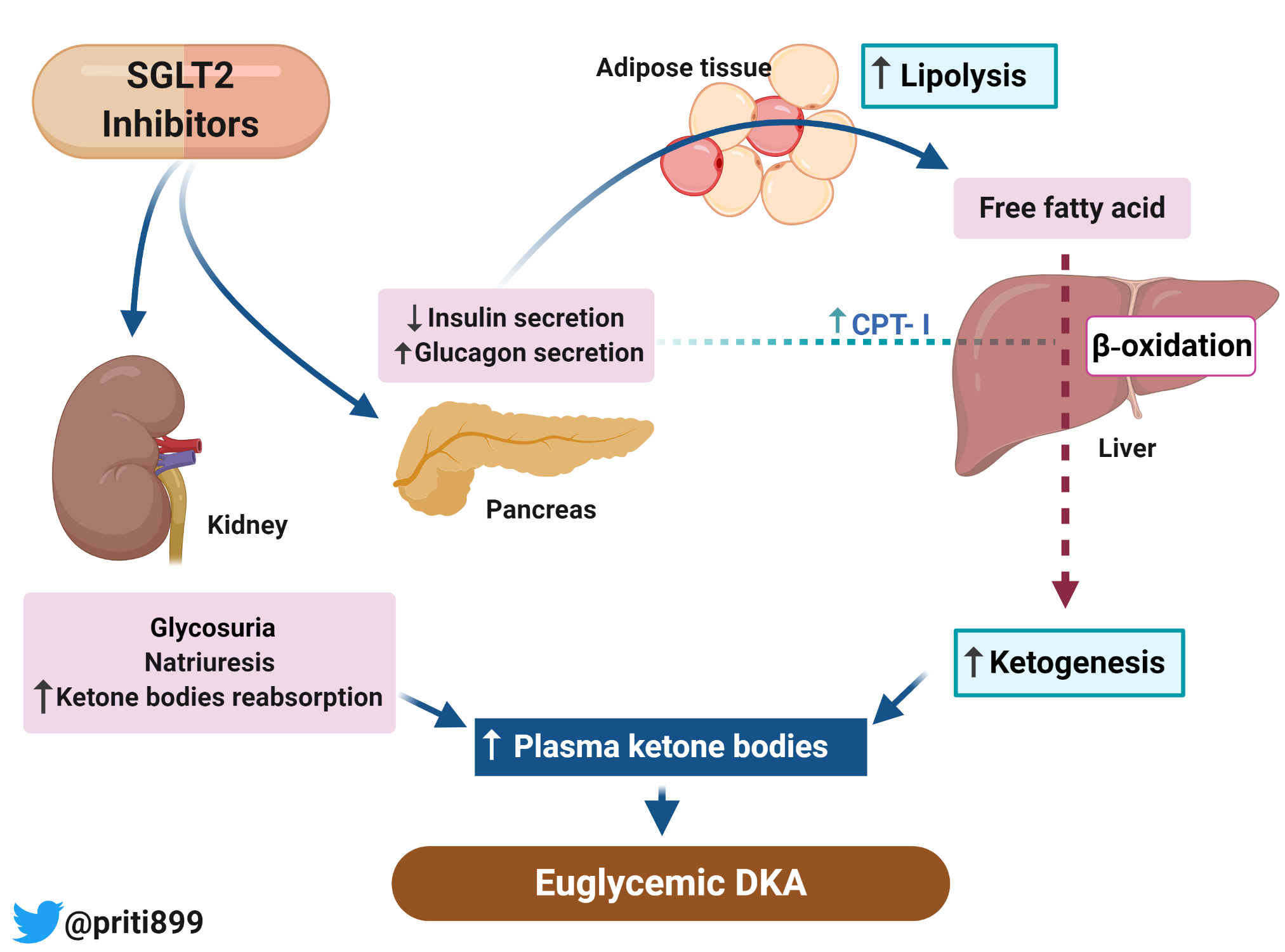 www.renalfellow.orgketoacidosis sglt2 euglycemic inhibitor induced urine sediment mitochondria principles transplantation immunologic bacterial forms renal renalfellow
www.renalfellow.orgketoacidosis sglt2 euglycemic inhibitor induced urine sediment mitochondria principles transplantation immunologic bacterial forms renal renalfellow
Blood Sugar Guide: Does High Blood Sugar Cause Ketoacidosis
 bloodsugarguides.blogspot.comWhy Does Diabetic Ketoacidosis Cause Dehydration — DiabetesCareTalk.net
bloodsugarguides.blogspot.comWhy Does Diabetic Ketoacidosis Cause Dehydration — DiabetesCareTalk.net
 www.diabetescaretalk.netketoacidosis diabetic dka pathophysiology dehydration acidosis mellitus hyperglycemia hypoglycemia diabetestalk metabolic disambiguation
www.diabetescaretalk.netketoacidosis diabetic dka pathophysiology dehydration acidosis mellitus hyperglycemia hypoglycemia diabetestalk metabolic disambiguation
What Is The Ketogenic Diet? - Perfect Keto Exogenous Ketones
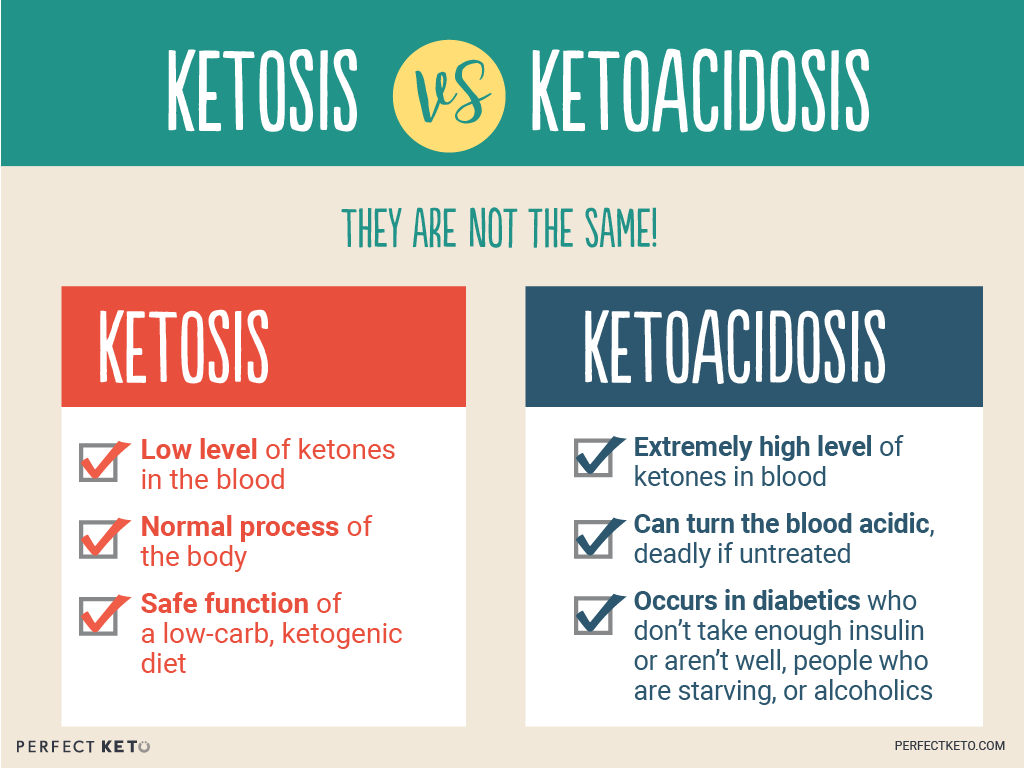 www.perfectketo.comketosis ketoacidosis keto diet vs fasting ketones intermittent ketone ketogenic between levels benefits level healthy fat high long dangerous timeline
www.perfectketo.comketosis ketoacidosis keto diet vs fasting ketones intermittent ketone ketogenic between levels benefits level healthy fat high long dangerous timeline
What is the ketogenic diet?. Blood sugar guide: does high blood sugar cause ketoacidosis. Ketoacidosis sglt2 euglycemic inhibitor induced urine sediment mitochondria principles transplantation immunologic bacterial forms renal renalfellow